For leaders who are impersonal they are. Fiedler argued that one should concentrate on helping people understand their particular leadership style and how to match that style to the particular situation rather than teaching people a particular leadership style.
The theory is based on the premise that each of us has one and only one leadership style which can be scored on the Least Preferred Co-worker LPC scale.

Fred fiedler leadership theory. Fiedlers contingency theory of leadership effectiveness was based on studies of a wide range of group effectiveness and concentrated on the relationship between leadership and organizational performance. However a psychologist Fred Fiedler introduced the contingency model of leadership in mid-1960 which states a leaders effectiveness is based on the situation. In the 1960s Fred Fiedler carried out research on the relationship contingency between the effectiveness of the leadership style and the situation.
Contingency theories in general state that the effectiveness of leadership depends upon the situation and there are numerous factors such as the nature of the task leaders personality and make-up of the group being led. Fielder Contingency theory According to the Fielder 1964 p153 he pointed out that there is no best leadership style but a leaders effectiveness is. According to him leadership effectiveness is contingent upon the situation.
What is the Fiedlers contingency model of leadership. The model states that there is no one best style of leadership. Fiedlers Contingency Theory of Leadership states that your effectiveness as a leader is determined by how well your leadership style matches the situation.
The Fiedler contingency model is a leadership theory of industrial and organizational psychology developed by Fred Fiedler born 1922 one of the leading scientists who helped his field move from the research of traits and personal characteristics of leaders to leadership styles and behaviours. With the Fiedler Contingency Model Fred Fiedler was the precursor of. Fred Fiedler was a scientist who studied the effectiveness of leaders in various group situations.
This is considered as one of the first model and leadership theories by Fiedler. He believes in a situational leadership style. Fiedler 19641967 broke through the idea of one single effective leadership style.
This relationship became to be known as the Fiedler contingency model. Clusters appeared to be more effective. Fiedler 1976 Changes in organizational leadership and the behavior of relationship- and task-motivated leaders Administrative Sci.
The Fiedler Contingency Model was created in the mid-1960s by Fred Fiedler a social scientist who studied the personality and characteristics of leaders. This is one of the earliest situation-contingent leadership theories given by Fiedler. The successful leader is one who adapts his style to the circumstance.
Fiedlers contingency theory was developed by Fred Fiedler in the late 1960s. For a thumb-in-the-wind approach to identifying leaders Fiedlers contingency theory can assist enormously. The Fiedler Contingency Model Explained.
This model appeared first in Fiedlers 1967 book A Theory of Leadership Effectiveness. Fiedler believes that there are two key types of the leader the task-oriented leader and the people-oriented leader. Instead a leaders effectiveness is based on the situation.
It was based on his studies of different group behaviors and the specific relationship between organizational performance and leadership. Fiedler believed that an individuals leadership style is the result of their experiences throughout the lifespan and therefore extremely difficult to change. Fiedlers contingency theory is a qualification or type of contingency theory.
The leaders leadership style and Situational favourableness. His research led him to develop the Fiedler Contingency Model in 1958 which states that a leaders ability to lead successfully depends on the control they wield over any given situation and their natural. Biography Fred Fiedler In 1938 at the age of 16 Fred Fiedler emigrated from Austria Vienna to the United States.
The interaction between leadership style and situation predicts the effectiveness of leadership behavior. Fiedlers Contingency TheoryPros The theory is extremely well researched given the stated parameters. The essence of Fiedlers theory is that a leaders effectiveness depends on a combination of two forces.
Leaders with good personal relations are matched to a poorly structured task environment. Fiedler called the combination of leadership style and situational favourableness Situational Contingency. Google Scholar ISI.
The model states that there is no one best style of leadership. A Theory of Leadership Effectiveness Volume 10 A Theory of Leadership Effectiveness Fred Edward Fiedler McGraw-Hill series in management. The Fiedler Contingency Model was created in the mid-1960s by Fred Fiedler a scientist who studied the personality and characteristics of leaders.
Fiedler devised Fiedlers contingency model or theory of leadership in 1958. 433 - 472. Instead a leaders effectiveness is based on the situation.
Fred Fiedler is the founder of the contingency theory that shows the relationship contingency between leadership effectiveness and situational circumstances. He studied at the University of Chicago. According to him if an organization attempts to.
Introduction Erik Erikson was an ego psychologist. Erik Eriksons theory of personality 1.
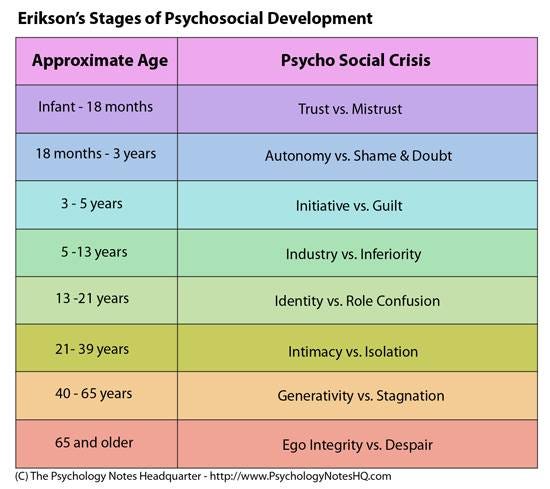
 The 8 Erikson Stages Of Psychosocial Development
The 8 Erikson Stages Of Psychosocial Development
Erik Eriksons theory of psychosocial development is one of the best-known theories of personality in psychology.

Erik erikson theory of personality. Erik Erikson reinterpreted Freuds psychosexual theory by incorporating the social aspect. Erik Erikson maintained that personality develops in a predetermined order and builds upon each previous stage. Much like Sigmund Freud Erikson believed that personality develops in a series of stages.
Structural Model of Personality. Eriksons best-known work is his theory that each stage of life is associated with a specific psychological struggle a struggle that contributes to a major aspect of personality. One of the main elements of Eriksons theory is the development of ego identity.
Eriksons theory involves a total of eight stages with each stage centering on a particular crisis of development. These eight stages of man or the psychosocial crises are plausible and insightful descriptions of how personality develops but at present they are descriptions only. He shifted from Freuds emphasis on psychosexual conflicts to one of psychosocial crises which have unique manifestations through adulthood and old age.
Erik Eriksons Stages of Social-Emotional Development. Much like Sigmund Freud Erikson believed that personality develops in a series of stages. Erik Eriksons TheoryTheory of Psychosocial Stages 2.
Erik Erikson And His Theory Of Personality Development Erik Erikson was born on July 15 1902 was a German psychoanalyst of German origin well known for his contributions psychology. During this stage adolescents search for a sense of self and personal identity through an intense exploration of personal values beliefs and goals. His now well-known stages of psychosocial development consists of eight which he theorized a person should pass through from infancy to late adulthood.
It was developed by Erik Erikson in the nineteen hundreds. The fifth stage of Erik Eriksons theory of psychosocial development is identity vs. His developmental progression from trust to autonomy initiative industry identity intimacy generativity and integrity was conceived as the sequential reorganization of ego and character structures.
But Erikson rejected Freuds attempt to describe personality solely on the basis of sexuality and unlike Freud felt that personality. While his theory was impacted by psychoanalyst Sigmund Freuds work Eriksons theory centered on psychosocial development rather than psychosexual development. He accepted many of Freuds theories including the id ego and superego and Freuds theory of infantile sexuality.
The stages that make up his theory are as follows. Erik Eriksons theory of psychosocial development is one of the best-known theories of personality in psychology. The psychodynamic theories of personality are mainly composed of famous theorists such as Sigmund Freud Erik Erikson and Alfred Adler.
Unlike Freuds theory of psychosexual stages Eriksons theory describes the impact of social experience across the whole lifespan. Erik Homburger Erikson born Erik Salomonsen. He argued that social experience was valuable throughout life with each stage recognizable by the specific conflict we encounter between our psychological needs and the surrounding social environment.
Erik Eriksons 1958 1963 psychosocial development theory proposes that our personality develops through eight stages from infancy to old age. It occurs during adolescence from about 12 to 18 years. Erikson believed that childhood is very important in personality development.
Erikson is a noted American sociologist. The personality theory that I have chosen to focus on will be Identity Theory. Erikson emphasized that the ego makes positive contributions to development by mastering attitudes ideas and skills at each stage of development.
Personality development according to Erikson is the ongoing product of the interaction of our individual needs with social expectations. Unlike Freuds theory of psychosexual stages Eriksons theory describes the impact of social experience across the whole lifespan. 15 June 1902 12 May 1994 was a German-American developmental psychologist and psychoanalyst known for his theory on psychological development of human beings.
During this stage adolescents develop a personal identity and a sense of self. Role confusion and it occurs during adolescence from about 12-18 years. Its origins are mysterious because his biological father was an unknown Dane.
The fifth stage of Eriksons theory of psychosocial development is the identity versus role confusion stage. Erik Erikson believed that every individual goes through a certain number of stages to reach his or her full development or potential Erikson 1994. Erik Erikson was an ego psychologist who developed one of the most popular and influential theories of development.
Erik Erikson is one of the few personality theorists from a Western perspective who addressed the entire lifespan. Erikson believed that humans personalities continued to develop past the age of five and he believed that the development of personality depended directly on the resolution of existential crises like trust autonomy intimacy individuality integrity and identity which were viewed in traditional psychoanalytic theory as mere by-products. Erik Erikson 19021994 was a stage theorist who took Freuds controversial theory of psychosexual development and modified it as a psychosocial theory.
He may be most famous for coining the phrase identity crisisHis son Kai T. We possess at best rudimentary and tentative knowledge of just what sort of environment will result for example in. Erik Eriksons theory of psychosocial development is one of the best known theories of personality in psychology.
Lets see how each theory explains the nature and process of personality. Despite lacking a bachelors degree Erikson served as a professor. He emphasized the role of culture and society and the conflicts that can take place within the ego itself.
A 20th century psychologist who developed the concept of identity crisis Erik Erikson made an impact on psychological theories by expanding Sigmund Freuds original five stages of development. The Object Relations Theory also belongs to this group of personality theories.
The fifth stage of Erik Eriksons theory of psychosocial development is identity vs. The first stage of Eriksons theory of psychosocial development occurs between birth and 1 year of age and is the most fundamental stage in life.
 Erickson S Theory Of Development Erickson Stages Of Development Stages Of Psychosocial Development Eriksons Stages Of Development
Erickson S Theory Of Development Erickson Stages Of Development Stages Of Psychosocial Development Eriksons Stages Of Development
Erikson was a student of Freuds and expanded on his theory of psychosexual development by emphasizing the importance of culture in parenting practices and motivations and adding three stages of adult development Erikson 1950.
Erik erikson's theory of psychosocial development. When people complete this stage successfully they come away with safe. Erik Eriksons 1958 1963 psychosocial development theory proposes that our personality develops through eight stages from infancy to old age. Erik Eriksons Theory of Psycho-social Development.
His contribution to the field includes an understanding of psychosocial development of humans. Each of the psychosocial stages is distinguished by two opposing emotional forces known as contrary dispositions that result in a crisis that needs to be resolved. Each stage is defined by a central crisis that the individual must grapple with to move on to the next stage.
Erikson is most well-known for his theory of psychological development of children as they grew into adulthood. He argued that social experience was valuable throughout life with each stage recognizable by the specific conflict we encounter between our psychological needs and the surrounding social environment. He presented these crises as 8 stages of psychosocial conflicts often known as the 8 Erikson stages.
Eriksons stages of psychosocial development as articulated in the second half of the 20th century by Erik Erikson in collaboration with Joan Erikson is a comprehensive psychoanalytic theory that identifies a series of eight stages that a healthy developing individual should pass through from infancy to late adulthoodErikson published a book called Childhood and Society around the 1950s. Eriksons wonderful theory helps to tell us why. Erikson asserts in his psychosocial theory that ego identity is reached by facing goals and challenges throughout eight stages of development over the entire life cycle.
His theory comprises of 8 stages that a healthy individual passes through in his lifetime each detailing a specific challenge or task. Erik Erikson Erik Erikson is possibly the best known of Sigmund Freuds many followers. In 1933 when Hitler was in power of Germany Erikson immigrated to the U.
Role confusion and it occurs during adolescence from about 12-18 years. Eriksons Stages of Psychosocial Development is a theory introduced in the 1950s by the psychologist and psychoanalyst Erik Erikson. Because an infant is utterly dependent developing trust is based on the dependability and quality of the childs caregivers.
Erik Erikson the famous psychoanalyst developed the theory of psycho-social development which deals with normal development over the entire life span of human beings. The second stage of Eriksons theory of psychosocial development takes place during early childhood and is focused on children developing a greater sense of personal control. It built upon Freuds theory of psychosexual development by drawing parallels in childhood stages while expanding it to include the influence of social dynamics as well as the extension of psychosocial development into adulthood.
And began teaching at Harvard University. Erik Erikson was a developmental psychologist who lived through the 1900s. He was born in Germany and died in Massachusetts.
Life is a serious of lessons and challenges which help us to grow. Psychoanalyst Erik Eriksons stages of psychosocial development theorize a model of human psychological growth made up of eight stages that cover the entire lifespan from birth to old age. Each of the eight Erikson stages is characterized by two contradictory emotional forces known as contrary dispositions usually.
Eriksons Psychosocial Theory Now lets turn to a less controversial psychodynamic theorist the father of developmental psychology Erik Erikson 1902-1994. Theory of Erik Erikson Eriksons eight stages of developmen t are said to be influenced by Freuds theories. Erikson married a dance teacher Joan Searson and had two children with the rise of the Nazis.
Erikson postulated that the development of an individual is the result of his interaction with his social environment. 2 Like Freud Erikson believed that toilet training was a vital part of this process. During this stage adolescents search for a sense of self and personal identity through an intense exploration of personal values beliefs and goals.
Erik Eriksons psychosocial development theory proposed that throughout our lives we encounter certain crises that contribute to our psychosocial development. The theory is helpful for child development and adults too. He also graduated from the University of Vienna with a teaching degree in 1930.
Eriksons stages of psychosocial development refer to a comprehensive psychoanalytical theory that identifies a series of stages a healthy individual must experience throughout their lifetime. He grew up in Europe and spent his young adult life under the direction of Freud. Erik eriksons psychosocial crisis life cycle model - the eight stages of human development Eriksons model of psychosocial development is a very significant highly regarded and meaningful concept.
The psychosocial challenge now according to Erikson is to build long-term loving relationships that feel safe. Each stage is characterized by a psychosocial crisis of two conflicting forces. Erikson did not focus so much on ages but on the progression of the self.
In 1950 Erik Erikson released his book Childhood and Society which outlined his now prominent Theory of Psychosocial Development.
Finding out what people want from their jobs what motivates them to keep working was the basis for a study by Fredrick Herzberg during the 1950s and 60s. He did this by asking people to describe work situations that made them feel really good about their jobs and situations in which they felt bad about them.
 Sources Of Employee Motivation Understanding The Two Factor Theory
Sources Of Employee Motivation Understanding The Two Factor Theory
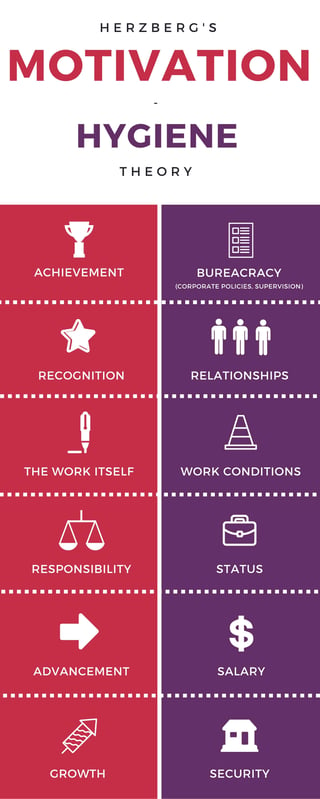
On the other hand the term hygiene is used by Herzberg to identify dissatisfiers because he considered such factors as necessary to be maintained.
Herzberg theory of motivation examples. Two-Factor Theory of Motivation Explained with Examples Frederick Herzberg extended the work of Maslow and developed a specific content theory of work motivation. Satisfaction Which is first and foremost the result of the motivator factors. Herzbergs Motivation Theory model or Two Factor Theory provides two factors that affect motivation in the workplace.
Another important contribution to our understanding of individual motivation came from Frederick Herzberg s studies which addressed the question What do people really want from their work experience In the late 1950s Herzberg surveyed numerous employees to find out. Herzbergs Two Factor Model of Motivation. An Integrative Literature Review Christina M.
The two-factor theory developed from data collected by. How do we motivate Employees. How do You Motivate Employees the conclusions he drew were extraordinarily influential and still form the bedrock of good motivational practice nearly half a century later.
Published in his famous article One More Time. Stello Department of Organizational Leadership Policy and Development College of Education and Human Development University of Minnesota Herzbergs Two-Factor Theory Abstract Herzberg published the two-factor theory of work motivation in 1959. Basically motivation factors include achievement recognition the work itself responsibility and advancement np.
According to Herzberg there are some job factors that result in satisfaction while there are other job factors that prevent dissatisfaction. In 1959 Frederick Herzberg a behavioural scientist proposed a two-factor theory or the motivator-hygiene theory. Motivation VS Movement Herzberg showed that Satisfaction and Dissatisfaction at work come from different factors It is possible to generate movement getting someone to do something through KITA mangement.
In 1959s he concluded that job satisfiers were related to job content and were allied to job context. Frederick Herzbergs Two Factor Theory of Motivation is a content model of motivation which says that satisfaction and dissatisfaction in work are created by different factors. Two Factor Theory is subject to bias.
Experiment or Research Study on Employees by Herzberg The two-factor theory also known as Herzbergs motivation-hygiene theory and dual-factor theory states that there are certain factors in the workplace that cause job satisfaction while a separate set of factors cause dissatisfaction. In 1959 Frederick Herzberg a behavioral scientist proposed a two-factor theory or the motivator-hygiene theory. Two Factor Motivational Theory People are.
In its essence the theory relates motivation and job satisfaction with a set of work-related factors and job dissatisfaction with a set of factors in the organisational. For example when an employee is satisfied they will give themselves credit for that satisfaction. 77 Herzbergs Motivator-Hygiene Theory.
Herzbergs view of satisfaction and dissatisfaction. The motivation and hygiene factors. These factors help magnify satisfaction but have slight effect on dissatisfaction.
There are many examples one could use to highlight the workings and logic to Herzberg motivation theory but the general concept is that in order to motivate an individual you have to do two things. Conversely when they are dissatisfied they will blame external factors. The Herzberg motivation theory comprises of two main strategies.
To increase job satisfaction in the workplace you may eliminate any and all hygiene factors that may cause dissatisfaction and low morale in the workplace. According to his theory people are influenced by two factors. You are a senior-level executive at a graphic design firm.
According to Herzberg the opposite of Satisfaction is No satisfaction and the opposite of. Herzbergs Two-Factor Theory of Job Satisfaction. By doing this you begin to make people neutral.
The motivation factors affect employees directly and it therefore is essential to focus on these factors to maximize the motivation initiative. Consider this example situation using the Herzberg theory. Herzberg uses the phrase motivating factors to describe things that when present have the ability to make individuals satisfied or even happy at work.
What are the basic components of Herzbergs motivator-hygiene theory. According to Herzberg there are some job factors that result in satisfaction while there are other job factors that prevent dissatisfaction. According to Herzberg the opposite of Satisfaction is No satisfaction and the opposite of Dissatisfaction is No Dissatisfaction.
These results form the basis of Herzbergs Motivation-Hygiene Theory sometimes known as Herzbergs Two Factor Theory. He wanted to find out how attitude affected employees motivation. Herzberg proposed the Motivation-Hygiene Theory also known as the Two factor theory 1959 of job satisfaction.
According to Herzberg Two-factor theory of motivation motivators for example challenging work the recognition of a persons accomplishments responsibility participation in decision-making processes the opportunity to do something meaningful the feeling of importance to an organization that offer positive satisfaction that comes from intrinsic conditions of the job itself such as recognition achievement or personal growth. Remove the demotivating factors Herzberg termed these as Hygiene factors. This is the case for Frederick Herzbergs two-factor theory of workplace motivation published in The Motivation to Work Herzberg Mausner and Snyderman in 1959.
Both men have continued to. The model also addresses the relationship between leadership style and subordinate maturity.
 Nepal In A Nut Shell Nepal Hersey And Blanchard S Situational Theory Business Leadership Leadership Leadership Models
Nepal In A Nut Shell Nepal Hersey And Blanchard S Situational Theory Business Leadership Leadership Leadership Models
Hersey further developed the Situational Leadership Model in his 1985 book The Situational Leader.

Hersey and blanchard's situational theory. Situational Leadership Theory of Hersey-Blanchard Explained The general belief of situational leadership theories is that leaders are products of real situations rather than gifts of nature. Blanchard and Hersey connect four different styles of leadership with four different stages of employees development here called Maturity Levels. Leadership style and the maturity level of those being led.
To Hersey and Blanchard there leadership styles stem from four basic behaviors designated with a letter-number combination. In doing so it becomes possible to lead any team to a successful outcome. Hersey-Blanchard Situational Theory The Hersey-Blanchard Situational Leadership Theory is a leadership theory conceived by Paul Hersey a professor who wrote a well known book Situational Leader and Ken Blanchard author of The One Minute Manager while working on the first edition of Management of Organizational Behavior now in its 9th edition.
The term situational leadership is most commonly derived from and connected with Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchards Situational Leadership Theory. Key Takeaways The Hersey-Blanchard Model suggests no leadership style is better than another. Therefore this theory is also known as the life-cycle theory of leadership.
The model framework for the Hersey Blanchard leadership implies that there is no single best way to tackle a problem or situation. The situational leader will make an optimal match between leadership style and maturity level. Readiness is the extent to which followers have the ability and willingness to accomplish a specific task.
During the mid-1970s life cycle theory of leadership was renamed Situational Leadership Theory Hersey and Blanchards model is considered as part of the larger Situational and Contingency Theories of Leadership of which Fiedlers C. It s also referred to as the Situational Leadership Model. And he continued to refine the Situational Leadership model and began to call it Situational Leadership II.
The theory developed by Paul Hersey and Kenneth Blanchard is based on the readiness level of the people the leader is attempting to influence. Blanchards first book The One-Minute Manager came out in 1982. According to the revised version of the theory effective leaders must base their behavior on the developmental level of group members for specific tasks.
The Hersey-Blanchard Model is also referred to as the Situational Leadership Model or Theory. Hersey-Blanchard Situational Leadership Theory The Hersey-Blanchard Situational Leadership Theory was created by Dr Paul Hersey a professor and author of The Situational Leader and Ken Blanchard author of the best selling The One-Minute Manager among others. The Hersey-Blanchard Situational Leadership Theory has two pillars.
During the mid-1970s it was renamed the Situational Leadership Theory. The three models are Fielders leadership model Houses path goal theory of leadership and Hersey and Blanchards situational leadership model. Even though Hersey and Blanchard worked together for years to support the notion that leadership styles should be situational they decided to go separate ways in 1977 to focus on their own agendas.
Situational Leadership II. Most people would agree that a good leader is a flexible one and this theory falls right in line with that manner of thinking. To purists there are important differences between the two models.
These theories mainly focus on task requirements peers expectation and behavior employees characteristics expectations and behavior. In 1979 ten years after launching the theory of all theories Blanchard left to start his own company now known as The Ken Blanchard Companies. Situational Leadership Theory or the Situational Leadership Model is a model created by Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchard developed while working on Management of Organizational Behavior.
This approach to leadership suggests the need to match two key elements appropriately. In the late 1970s and early 1980s the two developed their own styles. The Hersey-Blanchard situational leadership theory makes it possible for todays leaders to recognize the skills maturity and behaviors of their direct reports and adjust their leadership style to meet specific needs.
The four leadership styles introduced by. Blanchard decided to call his version of the model The Situational Leadership II Model or SLII Model. Hence the Hersey and Blanchard Situational Leadership Model Figure 1 which was originally labelled The Life Cycle Theory of Leadership has developed into two slightly divergent models.
The Situational Leadership Model by Blanchard Hersey. There are three major situation contingency models. The leaders leadership style and the followers maturity or preparedness levels.
The Hersey-Blanchard Model is a leadership model that focuses on the ability and willingness of individual employees. The model outlines four leadership styles each corresponding with a specific level of employee development. The theory states that instead of using just one style successful leaders.
The theory was first introduced in 1969 as life cycle theory of leadership. The Hersey-Blanchard model also known as the Hersey-Blanchard Situational Leadership Theory is a theory that advocates the existence of more than one optimum style of leadership. Hersey and Blanchards Situational Leadership Theory.
The Situational Leadership II or SLII model was developed by Kenneth Blanchard and builds on Blanchard and Herseys original theory. The Hersey Blanchard Situational Leadership Theory promotes flexible leaders that are able to match their style to the experience and ability of those they are leading.