Finding out what people want from their jobs what motivates them to keep working was the basis for a study by Fredrick Herzberg during the 1950s and 60s. He did this by asking people to describe work situations that made them feel really good about their jobs and situations in which they felt bad about them.
 Sources Of Employee Motivation Understanding The Two Factor Theory
Sources Of Employee Motivation Understanding The Two Factor Theory
On the other hand the term hygiene is used by Herzberg to identify dissatisfiers because he considered such factors as necessary to be maintained.
Herzberg theory of motivation examples. Two-Factor Theory of Motivation Explained with Examples Frederick Herzberg extended the work of Maslow and developed a specific content theory of work motivation. Satisfaction Which is first and foremost the result of the motivator factors. Herzbergs Motivation Theory model or Two Factor Theory provides two factors that affect motivation in the workplace.
Another important contribution to our understanding of individual motivation came from Frederick Herzberg s studies which addressed the question What do people really want from their work experience In the late 1950s Herzberg surveyed numerous employees to find out. Herzbergs Two Factor Model of Motivation. An Integrative Literature Review Christina M.
The two-factor theory developed from data collected by. How do we motivate Employees. How do You Motivate Employees the conclusions he drew were extraordinarily influential and still form the bedrock of good motivational practice nearly half a century later.
Published in his famous article One More Time. Stello Department of Organizational Leadership Policy and Development College of Education and Human Development University of Minnesota Herzbergs Two-Factor Theory Abstract Herzberg published the two-factor theory of work motivation in 1959. Basically motivation factors include achievement recognition the work itself responsibility and advancement np.
According to Herzberg there are some job factors that result in satisfaction while there are other job factors that prevent dissatisfaction. In 1959 Frederick Herzberg a behavioural scientist proposed a two-factor theory or the motivator-hygiene theory. Motivation VS Movement Herzberg showed that Satisfaction and Dissatisfaction at work come from different factors It is possible to generate movement getting someone to do something through KITA mangement.
In 1959s he concluded that job satisfiers were related to job content and were allied to job context. Frederick Herzbergs Two Factor Theory of Motivation is a content model of motivation which says that satisfaction and dissatisfaction in work are created by different factors. Two Factor Theory is subject to bias.
Experiment or Research Study on Employees by Herzberg The two-factor theory also known as Herzbergs motivation-hygiene theory and dual-factor theory states that there are certain factors in the workplace that cause job satisfaction while a separate set of factors cause dissatisfaction. In 1959 Frederick Herzberg a behavioral scientist proposed a two-factor theory or the motivator-hygiene theory. Two Factor Motivational Theory People are.
In its essence the theory relates motivation and job satisfaction with a set of work-related factors and job dissatisfaction with a set of factors in the organisational. For example when an employee is satisfied they will give themselves credit for that satisfaction. 77 Herzbergs Motivator-Hygiene Theory.
Herzbergs view of satisfaction and dissatisfaction. The motivation and hygiene factors. These factors help magnify satisfaction but have slight effect on dissatisfaction.
There are many examples one could use to highlight the workings and logic to Herzberg motivation theory but the general concept is that in order to motivate an individual you have to do two things. Conversely when they are dissatisfied they will blame external factors. The Herzberg motivation theory comprises of two main strategies.
To increase job satisfaction in the workplace you may eliminate any and all hygiene factors that may cause dissatisfaction and low morale in the workplace. According to his theory people are influenced by two factors. You are a senior-level executive at a graphic design firm.
According to Herzberg the opposite of Satisfaction is No satisfaction and the opposite of. Herzbergs Two-Factor Theory of Job Satisfaction. By doing this you begin to make people neutral.
The motivation factors affect employees directly and it therefore is essential to focus on these factors to maximize the motivation initiative. Consider this example situation using the Herzberg theory. Herzberg uses the phrase motivating factors to describe things that when present have the ability to make individuals satisfied or even happy at work.
What are the basic components of Herzbergs motivator-hygiene theory. According to Herzberg there are some job factors that result in satisfaction while there are other job factors that prevent dissatisfaction. According to Herzberg the opposite of Satisfaction is No satisfaction and the opposite of Dissatisfaction is No Dissatisfaction.
These results form the basis of Herzbergs Motivation-Hygiene Theory sometimes known as Herzbergs Two Factor Theory. He wanted to find out how attitude affected employees motivation. Herzberg proposed the Motivation-Hygiene Theory also known as the Two factor theory 1959 of job satisfaction.
According to Herzberg Two-factor theory of motivation motivators for example challenging work the recognition of a persons accomplishments responsibility participation in decision-making processes the opportunity to do something meaningful the feeling of importance to an organization that offer positive satisfaction that comes from intrinsic conditions of the job itself such as recognition achievement or personal growth. Remove the demotivating factors Herzberg termed these as Hygiene factors. This is the case for Frederick Herzbergs two-factor theory of workplace motivation published in The Motivation to Work Herzberg Mausner and Snyderman in 1959.
In this article you will discover Herzbergs theory of the two factors on work motivation which is also called the theory of motivation and hygiene. Read this book using Google Play Books app on your PC android iOS devices.
 Motivation To Work Amazon Co Uk Herzberg Frederick Etc 9780471373896 Books
Motivation To Work Amazon Co Uk Herzberg Frederick Etc 9780471373896 Books
Frederick Herzberg 1923-2000 was a clinical psychologist and is one of the major writers in management and motivational theories.

Motivation to work herzberg. Frederick Herzbergs theory of the two factors. Motivation to Work - Ebook written by Frederick Herzberg. Herzbergs Theory of Motivation tries to get to the root of motivation in the workplace.
To be more precised Frederic Herzbergs book The motivation to work 1959 including Motivation- Hygiene theory and Douglas McGregors book The human Side of Enterprise 1960 including Theory X and Theory Y are those kind of a research works. Herzberg had close links with Maslow and believed in a two-factor theory of motivationHe argued that there were certain factors that a business could introduce that would directly motivate employees to work harder motivatorsHowever there were also factors that would de-motivate an employee if not present but would not in themselves actually motivate employees to work harder hygienefactors. A close examination of Herzbergs model indicates that for those employees who have achieved a level of social and economic progress in the society higher-level needs of Maslows model esteem and self-actualization are the primary motivators.
The hygiene-motivation theory KITA was used by Herzberg to explain why managers dont motivate employees. Frederick Herzberg and his staff based their motivationhygiene theory on a variety of human needs and applied it to a strategy of job enrichment that has widely influenced motivation and job design strategies. ArticleMeltzer1960TheMT titleThe Motivation to Work authorL.
These elements were called hygiene. Frederick Herzberg and his staff based their motivationhygiene theory on a variety of human needs. Although Herzberg is most noted for his famous hygiene and motivational factors theory he was essentially concerned with peoples well -being at work Herzberg 1968.
Frederick Herzberg and his staff based their motivationhygiene theory on a variety of human needs. Similarities of Maslow and Herzberg Theory of Motivation. In the theory of the two factors or theory of motivation and hygiene Herzberg establishes that workers in reality all individuals have a series of needs.
To create satisfaction Herzberg says you need to address the motivating factors associated with work. Motivation to Work is a landmark volume that is of enduring interest to sociologists psychologists labor studies specialists and. Herzbergs distinction between motivation internally generated action and movement the response to external reward or punishment is paramount to understanding how employees experience the work world.
The two factors identified by Herzberg are motivators and hygiene factors. Herzberg developed the theory in an effort to better understand an employees attitude motivation and overall satisfaction in the workplace. Finding out what people want from their jobs what motivates them to keep working was the basis for a study by Fredrick Herzberg during the 1950s and 60s.
Examples of Herzbergs hygiene needs or maintenance factors in the workplace are. Underpinning his theories and academic teachings he was basically attempting to bring more humanity and caring into the workplace. The presence of motivators causes employees to work harder.
People are only truly motivated by enabling them to reach for and satisfy the factors that Herzberg identified as real motivators such as achievement advancement development etc which represent a far deeper level of meaning and fulfilment. Download for offline reading highlight bookmark or take notes while you read Motivation to Work. There is a great similarity between Maslows and Herzbergs models of motivation.
Things to consider include. Motivation and performance are not merely dependent upon environmental needs and external rewards. The Motivation to Work.
His approach focuses on content theories and explains specific things that motivate an individual at work. Providing opportunities for achievement. He called this job enrichment His premise was that every job should be examined to determine how it could be made better and more satisfying to the person doing the work.
His work invites us to consider that motivation comes from within the individual -- it is something the organization gets FROM its people rather than something it does TO them. Mausner and Barbara Bloch Snyderman journalIndustrial and Labor Relations Review year1960 volume13 pages470. Motivation and performance are not merely dependent upon environmental needs and external rewards.
Frederick Herzberg and his staff based their motivationhygiene theory on a variety of human needs and applied it to a strategy of job enrichment that has widely influenced motivation and job design strategies. You can leverage this theory to help you get the best performance from your team. He was one of the most influential management teachers and consultants of the post-world war II.
He did this by asking people to describe work situations that made them feel really good about their jobs and situations in which they felt bad about them. These are the needs classified as basic by the author specifically they are motivation and hygiene hence the name of his theory. He demonstrated that employees are not motivated by being kicked figuratively speaking or by being given more money or benefits a comfortable environment or reducing time spent at work.
He wanted to find out how attitude affected employees motivation. Motivation and performance are not merely dependent upon environmental needs and external rewards. Through Herzbergs studies he aimed to identify which factors contributed to satisfaction and which contributed to dissatisfaction.
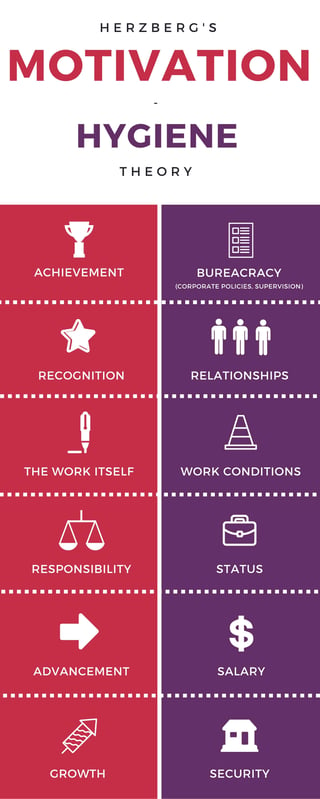
Herzbergs motivators and hygiene factors Achievement to advancement are motivators. The basis of the theory is that the factors operate independently of each other and thus need to be addressed by different methods.
 Herzberg S Two Factor Theory Organizational Behavior And Human Relations
Herzberg S Two Factor Theory Organizational Behavior And Human Relations
The 2008 graph diagram is based on the total percentages of First-Level factors arising in Herzbergs 1959 research of high and low attitude events among 200 engineers and accountants encompassing short and long duration feelings.
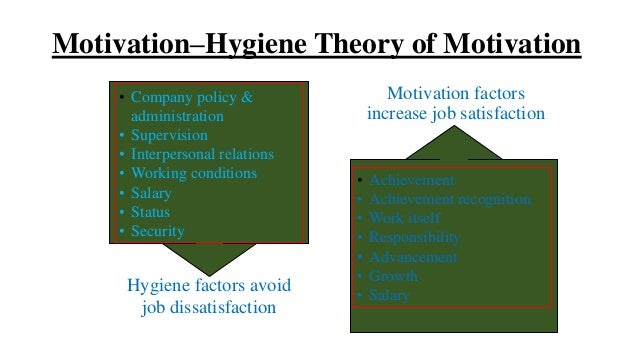
Herzberg hygiene factors and motivators graph diagram. The two-factor theory also known as Herzbergs motivation-hygiene theory states that there are certain factors in the workplace that cause job satisfaction while a separate set of factors cause dissatisfaction. This theory emphasizes on two set of factors- one set of factors which results in job satisfaction and another set of factors that causes job dissatisfaction. What is the Herzberg Two Factor Theory of Motivation.
The absence of hygiene factors will cause employees to work less hard. Herzbergs Two Factor Theory. Herzberg also coined the term job enrichment a technique which grew out of the hygiene-motivation theory.
Sometimes called the Two-Factor or Dual-Factor theory Herzbergs Motivational-Hygiene Theory relates some factors in the work are create job satisfactions while other factors contribute to job dissatisfaction. In 1959 Frederick Herzberg a behavioural scientist proposed a two-factor theory or the motivator-hygiene theory. In Figure 117 we have presented the essence of Herzberg theory using a diagram.
How do You Motivate Employees the conclusions he drew were extraordinarily influential and still form the bedrock of good motivational practice nearly half a century later. This collection of ready-to-use PPT graphic presentation of the Herzbergs Two Factor Theory of Motivation for PowerPoint contains 18 Creative and fully editable slides. Herzbergs Two Factor Theory of Motivation Evaluation.
The two factors identified by Herzberg are motivators and hygiene factors. Published in his famous article One More Time. The graph diagram is also available in MSPowerpoint slide fomat.
The crux of the two-factor theory of motivation therefore is that managers should cater to both satisfiers and dissatisfies. The first group of factors he called hygiene factors and the second motivators. A birds eye view of Herzbergs two factor theory can be had with the help of the simple diagram.
The others are hygiene factors. It was developed by Frederick Herzberg a psychologist who theorized that job satisfaction and job dissatisfaction act independently of each other. Herzberg aimed to dissect employees attitudes to their jobs to discover what prompted these attitudes and what impact they had on the person and their motivation to work.
The two-factor theory developed from data collected by. The mere improvement of hygiene factors cannot guarantee a motivating environment. Based on percentages of total factors causing high and low attitude effects.
Following are the chief merits of Herzbergs theory. Herzberg - The Motivation To Work 1959 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 ev e m e nt r e co g t i o n wo r k i t s e lf r e sp o ns i b lit y ad v n t s a. Herzbergs hygiene factors and motivators graph diagram ppt slide format.
Herzbergs Two-Factor Theory of Motivation. Herzbergs motivation-hygiene theory also known as the two-factor theory states that there are certain factors in the workplace that cause job satisfaction while a separate set of factors cause dissatisfaction and these factors act independently of each other. He called the factors that really motivate and satisfy a person in the workplace as Motivators and referred to the factors that lead to dissatisfaction as the hygiene factors.
It is rather a hygiene factor. Herzberg argued that there are two factors which are essential in the motivation of employees. This American psychologist who was very interested in peoples motivation and job satisfaction came up with the theory.
The hygiene-motivation or two factor theory resulted from research with two hundred Pittsburgh engineers and accountants. Herzberg hygiene factors and motivators graph diagram Herzberg diagram rocket and launch pad analogy diagram The 2008 diagram is based on the total percentages of First-Level factors arising in Herzbergs 1959 research of high and low attitude events among 200 engineers and accountants encompassing short and long duration feelings. IAccording to this theory money is not a motivator.
This theory also called the Motivation-Hygiene Theory or the dual-factor theory was penned by Frederick Herzberg in 1959. These results form the basis of Herzbergs Motivation-Hygiene Theory sometimes known as Herzbergs Two Factor Theory. Experiment or Research Study on Employees by Herzberg The two-factor theory also known as Herzbergs motivation-hygiene theory and dual-factor theory states that there are certain factors in the workplace that cause job satisfaction while a separate set of factors cause dissatisfaction.
According to Herzberg there are some job factors that result in satisfaction while there are other job factors that prevent dissatisfaction. Critical Evaluation of Herzbergs Theory. The presence of motivators causes employees to work harder.
Some factors in the workplace meet the first set of needs but not the second and vice versa. These encourage employees to work harder if present. Rather Herzberg used the term hygiene to describe factors that cause dissatisfaction in the workplace are extrinsic or independent of the work itself and are linked to things such as.
They are found within the actual job itself. These are motivators and hygiene factors. Examples of motivators include having an interesting job advancement and growth.
The psychologist Fredrick Herzberg introduced the Herzbergs Motivators and Hygiene factors also popular as the two-factor theory or a dual-factor theory.