Blooms taxonomy is a set of three hierarchical models used to classify educational learning objectives into levels of complexity and specificity. How many when where list define tell describe identify etc to draw out factual answers testing students recall and recognition.
 Bloom S Taxonomy Teaching Learning Everything In Between
Bloom S Taxonomy Teaching Learning Everything In Between
Blooms Taxonomy was created by Benjamin Bloom in 1956 published as a kind of classification of learning outcomes and objectives that have in the more than half-century since been used for everything from framing digital tasks and evaluating apps to writing questions and assessments.
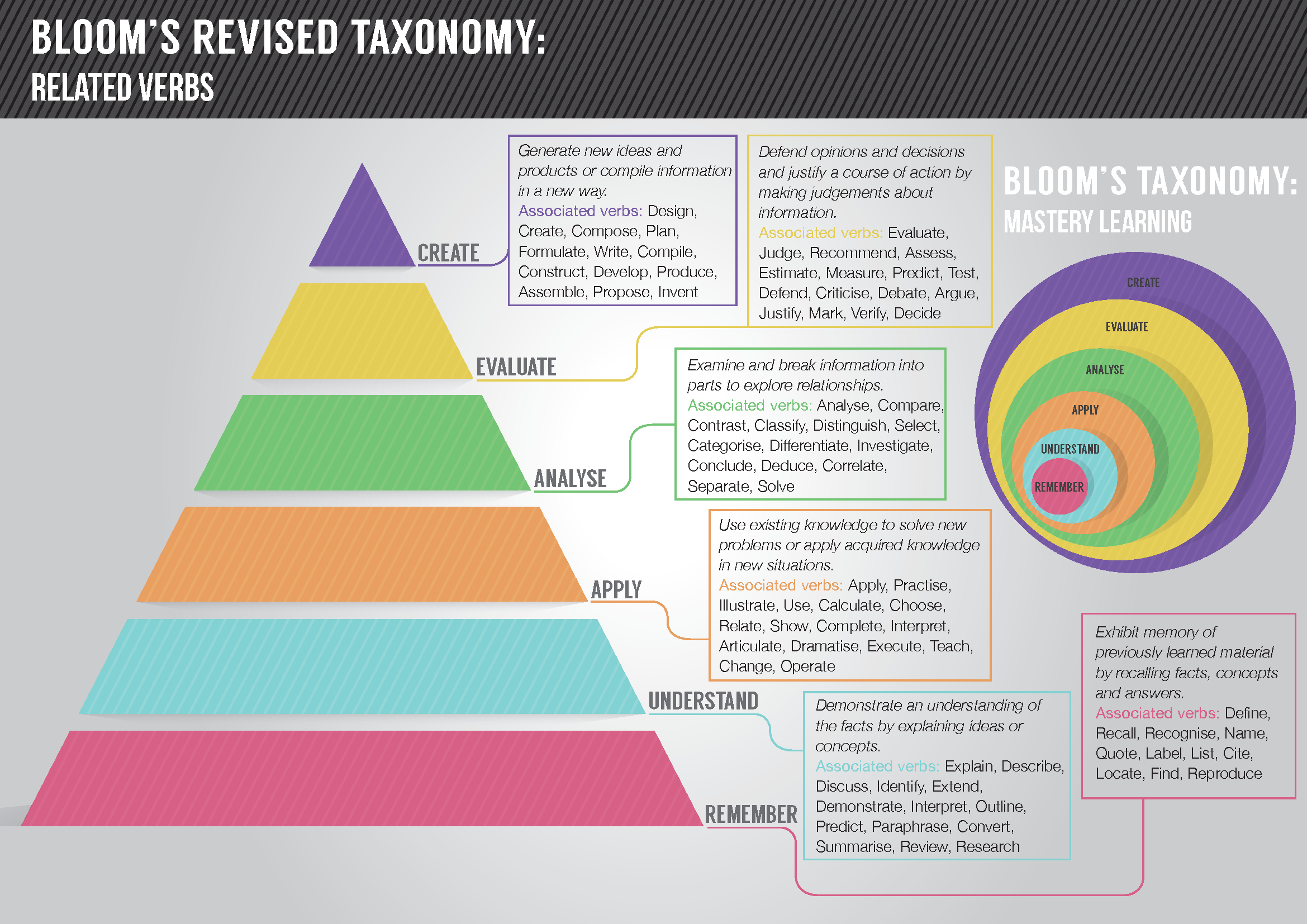
Overview of bloom's taxonomy. Blooms model consists of six levels with the three lower levels knowledge comprehension and application being more basic than the higher levels analysis synthesis and evaluation1. The models organize learning objectives into three different domains. They allow students to build on their prior understanding.
Make your own animated videos and animated presentations for free. Revising Blooms Taxonomy The Knowledge dimension Like the original the knowledge categories of the revised Taxonomy cut across subject matter lines. In brief Blooms taxonomy is a series of cognitive skills and learning objectives arranged in a hierarchical model.
Some think of the levels as a stairway in which learners are encouraged to achieve a higher level of thinking. According to the revised version of Blooms Taxonomy there are six cognitive learning. Blooms cognitive taxonomy originally was represented by six different domain levels.
Blooms Revised Taxonomys Usage in Assessment They are helpful because some verbs are appropriate at a particular level. Blooms taxonomy is hierarchical and often displayed as a pyramid with learning at the higher levels dependent on having attained prerequisite knowledge and skills at lower levels. Three of them include the substance of the subcat-egories of Knowledge in the original framework.
We feel that having a good overview of Blooms taxonomy will improve your study skills but we also realise that most academic texts covering the taxonomy are very complex. PowToon is a free. Revised Blooms Taxonomy A group of cognitive psychologists curriculum theorists and instructional researchers and testing and assessment specialists published in 2001 a revision of Blooms Taxonomy with the title A Taxonomy for Teaching Learning and Assessment.
Well over half a century since its publication in 1956 Blooms framework for learning has been translated into 22 languages and despite being revised by a new team in 2000 still forms the basis of school curricula and teaching standards the world over. The levels go from simplest to complex. All of the Bloom domains focused on the knowledge and cognitive processes.
Blooms taxonomy is a set of three hierarchical models used to classify educational learning objectives into levels of complexity and specificity. The cognitive domain list has been the primary focus of most traditional education and is frequently used to structure curriculum learning objectives. Use words and phrases such as.
In this blog I touch upon the basics of Revised Blooms Taxonomy in contrast to Blooms Taxonomy. 1 knowledge 2 comprehension 3 application 4 analysis 5 synthesis and 6 evaluation. Blooms taxonomy the cognitive domain is a hierarchical arrangement of 6 processes where each level involves a deeper cognitive understanding.
Blooms framework divided educational objectives into three. We therefore hope to simplify Blooms taxonomy for you in our series of articles on Blooms Taxonomy so that you can improve your study skills. The new Knowledge dimension however contains four instead of three main categories.
What is Blooms Taxonomy and how it applies to teaching. Cognitive Affective and SensoryPsychomotor. These six levels are applying remembering analyzing understanding creating and evaluating.
Introduction While the usage of Blooms Taxonomy BT to nail the learning outcomes has been used for training over several decades the Revised Blooms Taxonomy RBT brings in an added dimension that enables it to be used more effectively to design eLearning. One criticism of the original model was its lack of a systematic rationale of construction something that was to some extent addressed in the 2001 version. A taxonomy is really just a word for a form of classification This taxonomy had permeated teaching and instructional planning for almost 50 years before it was revised in 2001.
The taxonomy was proposed by Benjamin Bloom in 1956 He was an educational psychologist at the University. Originally Blooms taxonomy was designed as a way of gauging competence by placing a students knowledge on one of 6 levels which are often represented visually in the form of a pyramid. Remember Understand Apply Analyse Evaluate Create.
The three lists cover the learning objectives in cognitive affective and sensory domains. Blooms work was originally published in 1956. Remembering or recalling appropriate previously learned information to draw out factual usually right or wrong answers.
These gentlemen are the primary authors of the revisions to what had become known as Blooms Taxonomy an ordering of cognitive skills. Blooms Taxonomy of Educational Objectives is a notable exception to this rule. According to Blooms Taxonomy human thinking skills can be broken down into the following six categories.
The original Taxonomy of Educational Objectives is commonly referred to as Blooms Taxonomy named after Benjamin Bloom who devised a system of categorizing and classifying student learning objectives SLOs.
Blooms Taxonomy is a language for teachers and educators. Blooms Taxonomy is a hierarchical representation of how to understand and remember a concept or any novel thing.
 Bloom S Taxonomy Teaching Learning Everything In Between
Bloom S Taxonomy Teaching Learning Everything In Between
Educators have typically used Blooms taxonomy to inform or guide the development of assessments tests and other evaluations of student learning curriculum units lessons projects and.

Significance of bloom's taxonomy. According to the revised version of Blooms Taxonomy there are six cognitive learning. A group of cognitive psychologists curriculum theorists and instructional researchers and testing and assessment specialists published in 2001 a revision of Blooms Taxonomy with the title A Taxonomy for Teaching Learning and AssessmentThis title draws attention away from the somewhat static notion of educational objectives in Blooms original title and points to a more. Blooms Taxonomy was created in 1956 under the leadership of educational psychologist Dr Benjamin Bloom in order to promote higher forms of thinking in education such as analyzing and evaluating concepts processes procedures and principles rather than just remembering facts rote learningIt is most often used when designing educational training.
Blooms taxonomy is significant because it lays out a framework for understanding the different levels of learning. Indeed the taxonomy was originally structured as a way of helping faculty members think about the different types of test items that could be used to measure student academic growth. The terminology has been recently updated to include the following six levels of learning.
These six levels are applying remembering analyzing understanding creating and evaluating. Blooms work was not only in a cognitive taxonomy but also constituted a reform in how teachers thought about the questioning process within the classroom. A Guide for Developing Behavioral Objectives.
The cognitive domain list has been the primary focus of most traditional education and is frequently used to structure curriculum learning objectives. Blooms Taxonomy was created by Benjamin Bloom in 1956 published as a kind of classification of learning outcomes and objectives that have in the more than half-century since been used for everything from framing digital tasks and evaluating apps to writing questions and assessments. The most important use of Blooms Taxonomy is that is a good heuristic for teachers to understand the varying levels of cognitive psychomotor and affective demand that teachers have as outcomes.
Blooms taxonomy was one of the most significant representations of those learning outcomes. The one summarised here is based on work by Harrow Harrow A. Blooms Taxonomy BT and the Revised Blooms Taxonomy RBT are used in eLearning to craft the learning architecture of an eLearning course.
Blooms Taxonomy BT proposed by Benjamin Bloom is one of the key theoretical frameworks for learning popularly applied in Instructional Design. Blooms Taxonomy is a classification of the different objectives and skills that educators set for their students learning objectives. The taxonomy was proposed in 1956 by Benjamin Bloom an educational psychologist at the University of Chicago.
Under the leadership of Dr. Blooms Taxonomy in short analyses and defines the relation between what and how a tutor or teacher frames a concept and how he or she imparts that to his or her disciple. Blooms taxonomy is a classification system used to define and distinguish different levels of human cognitionie thinking learning and understanding.
Blooms Taxonomy was established by Benjamin Bloom in 1956 published as a kind of classification of learning outcomes and aims that has in the more than a half-century since been used for everything from framing digital tasks and assessing apps to writing questions and assessments. THE SIGNIFICANCE OF BLOOMS TAXONOMY DYNAMICS AND ITS VISION IN TEACHING AND LEARNING Taxonomy is defined as a system of identification and classification of ideas items or living things within a group according to their differences and similarities. Benjamin Bloom Blooms Taxonomy was created in 1956 in order to promote high-level learning rather than rote learning.
The three lists cover the learning objectives in cognitive affective and sensory domains. They will often use this pyramid to create learning objectives for their classroom school or school district. In the kingdom of teaching taxonomy is more about the categorization of learning in action.
No taxonomy of this domain was compiled by Bloom and his coworkers several competing taxonomies have been created over the years since Blooms original books. Their framework soon became known as Blooms Taxonomy and provides a way of categorizing educational goals. Blooms Taxonomy of Learning Domains.
They are helpful because some verbs are appropriate at a particular level. What is Blooms Revised Taxonomy. Bloom tells us that students must master lower levels of learning before they can.
Blooms Revised Taxonomys Usage in Assessment. Blooms taxonomy is a set of three hierarchical models used to classify educational learning objectives into levels of complexity and specificity. In 1956 Benjamin Bloom and his team of collaborators published their book Taxonomy of Educational Objectives.
A Taxonomy of the Psychomotor Domain. Some think of the levels as a stairway in which learners are encouraged to achieve a higher level of thinking. Blooms model consists of six levels with the three lower levels knowledge comprehension and application being more basic than the higher levels analysis synthesis and evaluation.